
Group Influence
What is Group Influence?
Group Influence, or “Social Proof” describes the effect that other people’s choices have on our own. In circumstances where our preferences are not defined, the influence of group persuasion is particularly powerful. However, even when we have a pre-defined idea, information about the majority opinion can alter our behaviour.
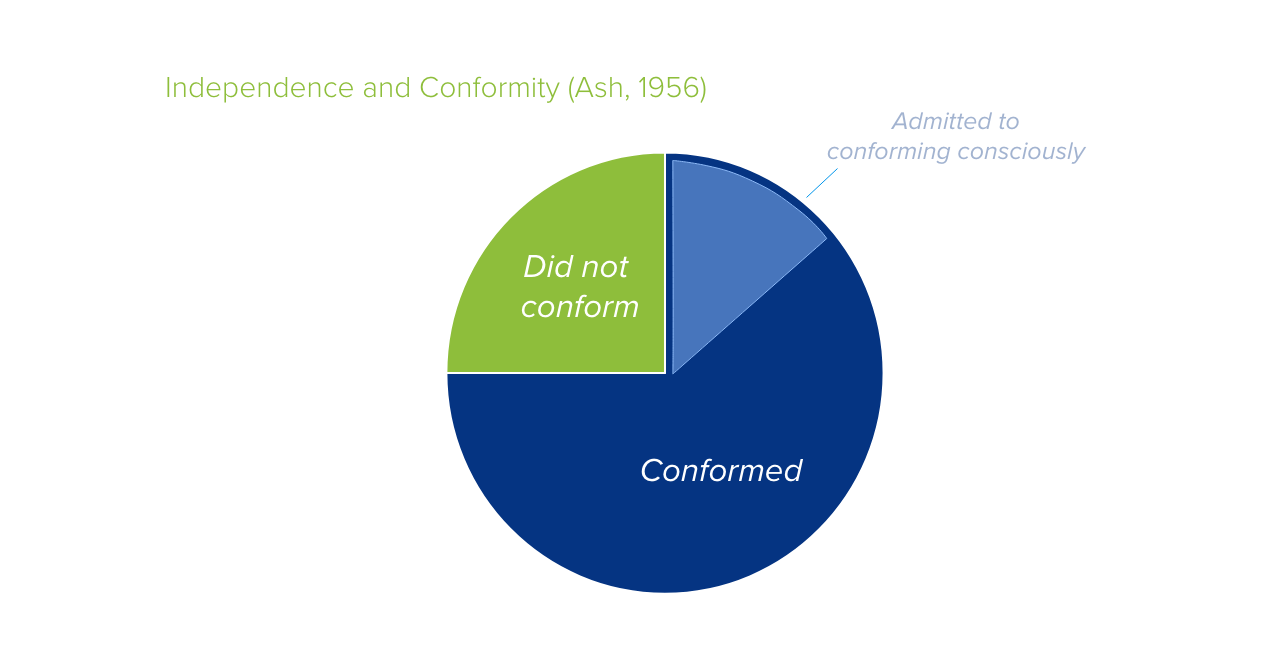
Explanations for our impressionability vary. In his 1956 group studies, Solomon Asch demonstrated three different responses in situations where subjects had predefined (obviously correct) judgements that conflicted with (obviously incorrect) group judgements:
- The participant did not conform at any stage (only 25%)
- The individual conformed due to fear of rejection (the majority)
- The individual was effectively persuaded of an obviously incorrect judgement
Examples
Group Influence and Social Proof are often used to give credibility to consumer offerings. For example, restaurants often maintain an unnecessary waiting list, and venues benefit from queues that run outside the building. Waiting staff occasionally remove a slice from a freshly baked cake in order to highlight its popularity.
Group Influence in Marketing
Displaying positive testimonials or high user numbers is a common strategy for marketers. Promotional offers that suggest an item is in high demand combine the effect of Group Influence with that of Scarcity.
The importance of demonstrating popularity and leveraging group influence is particularly significant for eCommerce because, unlike what happens in physical stores, past and present customers are invisible to online consumers. Platforms like Amazon apply sophisticated strategies for gathering user reviews and demonstrating their integrity. They have also developed a compelling set of visual signifiers that reassure and persuade consumers.
Group Influence
The urge to conform is a strong motivation and delivers a powerful sense of safety and security. It is most effective in situations where a customer is choosing between similar options. However, even more substantial decisions can be influenced by demonstrating the popularity of a particular choice.
